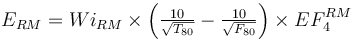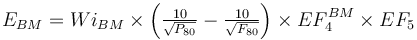Difference between revisions of "Model:Bond RMBM Model"
(Created page with "category:Models category:Specific Energy Models Category:Bond rod mill ball mill Model == Bond/Rowland rod mill ball mill model == This is a rod mill feeding a bal...") |
(→Secondary and tertiary crushers) |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
| + | ===Required parameters=== |
||
| − | == Secondary and tertiary crushers == |
||
| + | * '''F<sub>80</sub>, µm''' is the 80% passing size of the fresh feed to the circuit (expected to be a Bond-compatible size distribution). |
||
| + | * '''P<sub>80</sub>, µm''' is the 80% passing size of the circuit product (expected to be a Bond-compatible size distribution). |
||
| + | * '''Availability''', expressed as a decimal (0.90 = 90% availability) is used to convert t/h to t/d. |
||
| + | |||
| + | ===Optional parameters=== |
||
| + | * '''Description''' and '''Comment''' are optional text fields |
||
| + | * '''Maximum t/h limit''' is a t/h throughput above which a warning message is displayed (but does not actually limit the throughput). |
||
| + | * '''T<sub>80</sub> min''' and '''T<sub>80</sub> min''' override the transfer size restrictions built into the model |
||
| + | * [[Ball mill work index adjustment]] used to adjust Wi<sub>BM</sub> for different P<sub>80</sub> sizes. |
||
| + | ** '''coefficient (a)''', the fitted coefficient to the adjustment equation |
||
| + | ** '''exponent (b)''', the fitted exponent to the adjustment equation |
||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === Secondary and tertiary crushers === |
||
The model assumes any secondary and/or tertiary crushing happens upstream of the rod mill. Crusher specific energy is not included in this model. |
The model assumes any secondary and/or tertiary crushing happens upstream of the rod mill. Crusher specific energy is not included in this model. |
||
Revision as of 18:12, 26 April 2015
Contents
Bond/Rowland rod mill ball mill model
This is a rod mill feeding a ball mill model that estimates the specific energy consumption (ERM and EBM) using the Rowland interpretation of the classical Bond work index equation including Rowland efficiency factors.
Testwork Required
Formulae
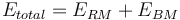
The rod mill oversize feed factor (EF4RM) is calculated using the greater of the sample's rod mill or crushing work index (which is usually the WiRM). The optimal feed size and EF4 are both calculated using whichever is greater.
![EF_4^{RM} =\left [ 1 + \left( \frac{ (0.907 \times Wi_{RM} - 7) }{ \left (\frac{F_{80} }{ T_{80}} \right )} \right) \left ( {\frac{F_{80} }{ { 16 000 \left(\frac{14.33}{Wi_{RM} } \right )^{0.5}}} }-1 \right ) \right ]](/images/math/2/7/c/27cb6782d414da805410db603189ef54.png)
The ball mill oversize feed factor (EF4BM) is always calculated with the ball mill work index. The optimal feed size for the EF4BM is always calculated using the rod mill work index.
![EF_4^{BM} =\left [ 1 + \left( \frac{(0.907 \times Wi_{BM} - 7) }{ \left (\frac{T_{80} }{ P_{80}} \right )} \right) \left ( {\frac{T_{80} }{ { 4000 \left(\frac{14.33}{Wi_{RM} } \right )^{0.5}}} }-1 \right ) \right ]](/images/math/3/4/e/34ec5343663db3e292e9c0623a6b2f89.png)
where:
- F80, µm is the specified circuit feed size (crushing plant product)
- T80, µm is the transfer size that balances the power draw in rod & ball mill stages.
- P80, µm is the specified product size (hydrocyclone overflow)
Required parameters
- F80, µm is the 80% passing size of the fresh feed to the circuit (expected to be a Bond-compatible size distribution).
- P80, µm is the 80% passing size of the circuit product (expected to be a Bond-compatible size distribution).
- Availability, expressed as a decimal (0.90 = 90% availability) is used to convert t/h to t/d.
Optional parameters
- Description and Comment are optional text fields
- Maximum t/h limit is a t/h throughput above which a warning message is displayed (but does not actually limit the throughput).
- T80 min and T80 min override the transfer size restrictions built into the model
- Ball mill work index adjustment used to adjust WiBM for different P80 sizes.
- coefficient (a), the fitted coefficient to the adjustment equation
- exponent (b), the fitted exponent to the adjustment equation
Secondary and tertiary crushers
The model assumes any secondary and/or tertiary crushing happens upstream of the rod mill. Crusher specific energy is not included in this model.
The choice of crushers and arrangement is normally based on volumetric flow and not on power draw. Use a crusher catalogue or another tool, like Metso's Bruno software, to determine the size and arrangement of the crushers ahead of the ball mill(s).