Difference between revisions of "Loveday/Barratt SAG model"
(Created page with "==History== Brian Loveday (1978) published a scale-up procedure for autogenous pilot plant power draw to industrial sized machines tha...") |
(No difference)
|
Revision as of 03:55, 5 December 2013
History
Brian Loveday (1978) published a scale-up procedure for autogenous pilot plant power draw to industrial sized machines that used an empirical power number to encompass all the motion effects of a mill charge. Derek Barratt (2002) derived a set of power numbers for industrial machines for use in Loveday's base formula, where a power number for a particular mill filling and speed are read from a chart and then charge density, including the ball load, are fed into Loveday's formula to predict SAG mill power draw.
The power numbers that Barratt published are based on mills with 'typical' cone-ends (probably 15° to 25°). A flat-ended (shell-supported) mill is expected to have 5% less power draw.
Model Form
Loveday's equation is:
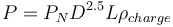
Where:
- P is the power evolved at the mill shell, kW
- PN is the empirical power number read from the chart below
- D is the mill diameter inside the effective liner thickness, m
- L is the mill effective grinding length (or 'belly length'), m
- ρcharge is the density of the mill charge, including balls, rocks and slurry, t/m3
The formula for ρcharge is as follows:
![\rho_{charge} = \left[\tfrac{J_{balls}}{J_{total}} \rho_{balls} + \tfrac{J_{ore}}{J_{total}} \rho_{ore} \right] \times \left( 1- J_{voids} \right) + J_{voids} \rho_{pulp}](/images/math/7/8/d/78d322f54f9ae3274998eb9def79b822.png)
Where:
- Jtotal is the fractional mill volumetric filling (eg. 0.30 for 30%)
- Jballs is the fractional volumetric filling of balls (eg. 0.10 for 10%)
- Jore is the fractional volumetric filling of coarse ore (eg. Jtotal - Jballs)
- Jvoids is the fractional volumetric void space between rocks and balls (use 0.4)
- ρballs is the density of the grinding balls, t/m3
- ρore is the density of the ore, t/m3
- ρpulp is the density of the pulp, excluding rocks and balls, t/m3