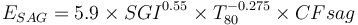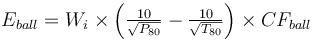Difference between revisions of "Model:Amelunxen SGI"
| (18 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[category:Models]] |
[[category:Models]] |
||
[[category:Specific Energy Models]] |
[[category:Specific Energy Models]] |
||
| − | [[ |
+ | [[category: Amelunxen SGI Model]] |
| + | [[Category: P80 adjustment]] |
||
== Amelunxen SGI Model == |
== Amelunxen SGI Model == |
||
| − | This is a SAG or AG mill plus ball mill |
+ | This is a model that estimates the specific energy consumption of a SAG or AG mill plus ball mill circuit using the equation by [[Bibliography:_Specific_energy_consumption_models|Amelunxen (2014)]] for E<sub>SAG</sub> and the classical Bond work index equation for E<sub>ball</sub> substituting ''CF<sub>ball</sub>'' in the place of the Rowland efficiency factors. |
The model requires manual calibration factors for both equations (''CF<sub>SAG</sub>'' and ''CF<sub>ball</sub>'', respectively) and is very sensitive to the settings used for these factors. |
The model requires manual calibration factors for both equations (''CF<sub>SAG</sub>'' and ''CF<sub>ball</sub>'', respectively) and is very sensitive to the settings used for these factors. |
||
| Line 11: | Line 12: | ||
* [[Testwork: SAG grindability index|SAG grindability index]] |
* [[Testwork: SAG grindability index|SAG grindability index]] |
||
* [[Testwork: Bond ball mill work index|Bond ball mill work index]] |
* [[Testwork: Bond ball mill work index|Bond ball mill work index]] |
||
| + | |||
| + | ===Required parameters=== |
||
| + | * '''F<sub>80</sub>, µm''' is the 80% passing size of the fresh feed to the circuit (expected to be a Bond-compatible size distribution). |
||
| + | * '''P<sub>80</sub>, µm''' is the 80% passing size of the circuit product (expected to be a Bond-compatible size distribution). |
||
| + | * '''Availability''', expressed as a decimal (0.90 = 90% availability) is used to convert t/h to t/d. |
||
| + | * Ball mill '''Operating strategy''' when circuit is SAG-limited (note, fixed speed can only be ''vary P<sub>80</sub>'') |
||
| + | |||
| + | ===Optional parameters=== |
||
| + | * '''Description''' and '''Comment''' are optional text fields |
||
| + | * '''Maximum t/h limit''' is a t/h throughput limit above which the mills will turn down by, for example, grinding out. |
||
| + | * '''T<sub>80</sub> min''' and '''T<sub>80</sub> min''' override the transfer size restrictions built into the model |
||
| + | * [[Ball mill work index adjustment]] used to adjust Wi<sub>BM</sub> for different P<sub>80</sub> sizes. |
||
| + | ** '''coefficient (a)''', the fitted Hukki coefficient to the adjustment equation (enter as a positive number) |
||
| + | * '''CFball calibration factor''', model tuning factor for E<sub>BM</sub> |
||
| + | * '''CFsag calibration factor''', model tuning factor for E<sub>ASAG</sub> |
||
===Formulae=== |
===Formulae=== |
||
| Line 17: | Line 33: | ||
<math>E_{ball} = W_i \times \left ( \tfrac {10}{\sqrt{ P_{80} }} - \tfrac {10}{\sqrt{ T_{80} }} \right ) \times CF_{ball} </math><sup>[[Bibliography:_Specific_energy_consumption_models|Becerra & Amelunxen, 2012]]</sup> |
<math>E_{ball} = W_i \times \left ( \tfrac {10}{\sqrt{ P_{80} }} - \tfrac {10}{\sqrt{ T_{80} }} \right ) \times CF_{ball} </math><sup>[[Bibliography:_Specific_energy_consumption_models|Becerra & Amelunxen, 2012]]</sup> |
||
| + | |||
| + | There is another model that has been published by F. Jorquera & M. Becerra (Procemin 2016) that was specifically calibrated to the El Soldado single-stage SAG mill (SS-SAG). They arrived at a 7% lower value for the coefficient (5.494 versus 5.9 in Amelunxen, 2014), and a slightly different exponent (0.563 versus 0.55 in Amelunxen). The exponent is within 2% of Amelunxen's value, and the model does not account for the way El Soldado rejects uncrushed pebbles from the SAG circuit, so the SGI of the feed is slightly harder than the actual work the mill is doing. Of interest is this single-stage SAG mill uses SGI to predict grinding down to about 200 µm with no need for a ball mill work index. |
||
| + | |||
| + | <math>E_\text{El Soldado} = 5.494 \times \left( \frac{SGI}{ \sqrt{T_{80}}} \right)^{0.5494} \times CFsag</math> |
||
| + | |||
| + | The Single Stage SAG model in SAGMILLING.COM uses Amelunxen's form of the equations as it is not normal to reject pebbles the way it is done at El Soldado. The pebble rejection probably reduces the E<sub>SAG</sub> by about 10% at El Soldado versus what would be observed with pebble recycle. |
||
===CF<sub>sag</sub> calibration factor=== |
===CF<sub>sag</sub> calibration factor=== |
||
| Line 23: | Line 45: | ||
* Base value, SAB circuit (no pebble crushing, ~6 inch SAG feed), CF<sub>sag</sub> = 1.00 |
* Base value, SAB circuit (no pebble crushing, ~6 inch SAG feed), CF<sub>sag</sub> = 1.00 |
||
* Pebble crushing, SABC circuit, CF<sub>sag</sub> = 0.85 |
* Pebble crushing, SABC circuit, CF<sub>sag</sub> = 0.85 |
||
| − | * Pre-crushing, (fine SAG feed, - |
+ | * Pre-crushing, (fine SAG feed, -120 mm SAG feed<sup>Custer et al, CMP 2001</sup>), CF<sub>sag</sub> = 0.90 |
| − | * Pre-crushing and pebble crushing, CF<sub>sag</sub> = 0.85 × 0.90 = 0.77 |
+ | * Pre-crushing and pebble crushing, CF<sub>sag</sub> = 0.85 × 0.90 = 0.77 |
===CF<sub>ball</sub> calibration factor=== |
===CF<sub>ball</sub> calibration factor=== |
||
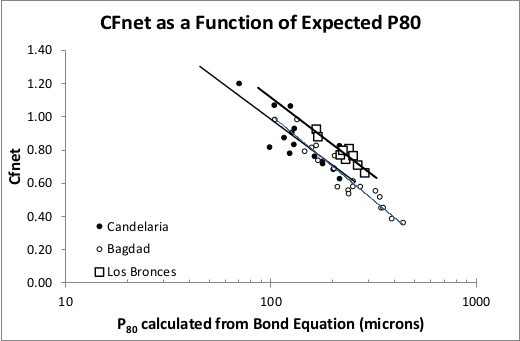
The ''CF<sub>ball</sub>'' is a manually picked value used to lump the [[phantom cyclone]] effect and the variety of Rowland efficiency factors into a single factor. This value is usually picked based on a mill survey, or taken from a diagram such as Figure 5 from Becerra & Amelunxen (2012)<sup>[[Bibliography: Specific energy consumption models#Amelunxen SGI Method|Bibliography]]</sup>, reproduced below. |
The ''CF<sub>ball</sub>'' is a manually picked value used to lump the [[phantom cyclone]] effect and the variety of Rowland efficiency factors into a single factor. This value is usually picked based on a mill survey, or taken from a diagram such as Figure 5 from Becerra & Amelunxen (2012)<sup>[[Bibliography: Specific energy consumption models#Amelunxen SGI Method|Bibliography]]</sup>, reproduced below. |
||
| + | |||
[[File:BecerraAmelunxen2012-CFnet v P80.png]] |
[[File:BecerraAmelunxen2012-CFnet v P80.png]] |
||
| + | |||
(CFnet is the term used by Becerra & Amelunxen for CF<sub>ball</sub>) |
(CFnet is the term used by Becerra & Amelunxen for CF<sub>ball</sub>) |
||
| + | |||
| + | If the CF<sub>ball</sub> value is left blank, then the fitted "Los Bronces" curve is used (squares in the Becerra & Amelunxen diagram). |
||
| + | |||
| + | CF<sub>ball</sub> = 2.35 - 0.29 × Ln(P<sub>80</sub>) |
||
===Transfer size=== |
===Transfer size=== |
||
| − | The transfer size assumed in a Amelunxen SGI model is described as being "as would be measured in a plant survey" (uncorrected for the extra fines, the [[phantom cyclone]] effect). This is different to the basis of the various Bond models where the transfer size is a synthetic value that implies the removal of the extra fines. |
+ | The transfer size assumed in a Amelunxen SGI model is described as being "as would be measured in a plant survey" (uncorrected for the extra fines, meaning no allowance for the [[phantom cyclone]] effect is requried). This is different to the basis of the various Bond models where the transfer size is a synthetic value that implies the removal of the extra fines. |
| − | In practical terms, running an SGI model will require relaxing the upper T80 constraints (the default constraints are tuned to the Bond models). Upper limits of 5000 µm or 6000 µm are not uncommon when simulating Andean copper porphyry type ores |
+ | In practical terms, running an SGI model will require relaxing the upper T80 constraints (the default constraints are tuned to the Bond models). Upper limits of 5000 µm or 6000 µm are not uncommon when simulating Andean copper porphyry type ores in SAB or SABC-A configurations. |
Latest revision as of 15:59, 30 August 2023
Amelunxen SGI Model
This is a model that estimates the specific energy consumption of a SAG or AG mill plus ball mill circuit using the equation by Amelunxen (2014) for ESAG and the classical Bond work index equation for Eball substituting CFball in the place of the Rowland efficiency factors.
The model requires manual calibration factors for both equations (CFSAG and CFball, respectively) and is very sensitive to the settings used for these factors.
Testwork Required
Required parameters
- F80, µm is the 80% passing size of the fresh feed to the circuit (expected to be a Bond-compatible size distribution).
- P80, µm is the 80% passing size of the circuit product (expected to be a Bond-compatible size distribution).
- Availability, expressed as a decimal (0.90 = 90% availability) is used to convert t/h to t/d.
- Ball mill Operating strategy when circuit is SAG-limited (note, fixed speed can only be vary P80)
Optional parameters
- Description and Comment are optional text fields
- Maximum t/h limit is a t/h throughput limit above which the mills will turn down by, for example, grinding out.
- T80 min and T80 min override the transfer size restrictions built into the model
- Ball mill work index adjustment used to adjust WiBM for different P80 sizes.
- coefficient (a), the fitted Hukki coefficient to the adjustment equation (enter as a positive number)
- CFball calibration factor, model tuning factor for EBM
- CFsag calibration factor, model tuning factor for EASAG
Formulae
There is another model that has been published by F. Jorquera & M. Becerra (Procemin 2016) that was specifically calibrated to the El Soldado single-stage SAG mill (SS-SAG). They arrived at a 7% lower value for the coefficient (5.494 versus 5.9 in Amelunxen, 2014), and a slightly different exponent (0.563 versus 0.55 in Amelunxen). The exponent is within 2% of Amelunxen's value, and the model does not account for the way El Soldado rejects uncrushed pebbles from the SAG circuit, so the SGI of the feed is slightly harder than the actual work the mill is doing. Of interest is this single-stage SAG mill uses SGI to predict grinding down to about 200 µm with no need for a ball mill work index.
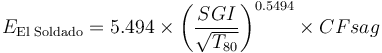
The Single Stage SAG model in SAGMILLING.COM uses Amelunxen's form of the equations as it is not normal to reject pebbles the way it is done at El Soldado. The pebble rejection probably reduces the ESAG by about 10% at El Soldado versus what would be observed with pebble recycle.
CFsag calibration factor
The CFsag factor is used to reflect the effect of pebble crushing and pre-crushing on the overall circuit performance.
- Base value, SAB circuit (no pebble crushing, ~6 inch SAG feed), CFsag = 1.00
- Pebble crushing, SABC circuit, CFsag = 0.85
- Pre-crushing, (fine SAG feed, -120 mm SAG feedCuster et al, CMP 2001), CFsag = 0.90
- Pre-crushing and pebble crushing, CFsag = 0.85 × 0.90 = 0.77
CFball calibration factor
The CFball is a manually picked value used to lump the phantom cyclone effect and the variety of Rowland efficiency factors into a single factor. This value is usually picked based on a mill survey, or taken from a diagram such as Figure 5 from Becerra & Amelunxen (2012)Bibliography, reproduced below.
(CFnet is the term used by Becerra & Amelunxen for CFball)
If the CFball value is left blank, then the fitted "Los Bronces" curve is used (squares in the Becerra & Amelunxen diagram).
CFball = 2.35 - 0.29 × Ln(P80)
Transfer size
The transfer size assumed in a Amelunxen SGI model is described as being "as would be measured in a plant survey" (uncorrected for the extra fines, meaning no allowance for the phantom cyclone effect is requried). This is different to the basis of the various Bond models where the transfer size is a synthetic value that implies the removal of the extra fines.
In practical terms, running an SGI model will require relaxing the upper T80 constraints (the default constraints are tuned to the Bond models). Upper limits of 5000 µm or 6000 µm are not uncommon when simulating Andean copper porphyry type ores in SAB or SABC-A configurations.