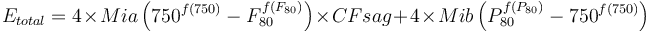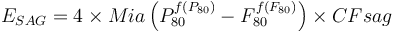Difference between revisions of "Model:Morrell Mi SMC SAG"
(→Formulae) |
(→Formulae) |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
===Formulae=== |
===Formulae=== |
||
The method is superficially similar to Bond (among other models), but with a variable exponent on size defined by: |
The method is superficially similar to Bond (among other models), but with a variable exponent on size defined by: |
||
| − | <math> |
+ | <math>f(x) = - 0.295 - \frac{x}{10^6}</math> |
Where ''x'' is the particle 80% passing size in µm. |
Where ''x'' is the particle 80% passing size in µm. |
||
| − | <math>E_{total} = 4 \times Mia \left( 750^{ |
+ | <math>E_{total} = 4 \times Mia \left( 750^{f(750)} - F_{80}^{f(F_{80})} \right) \times CFsag + 4 \times Mib \left( P_{80}^{f(P_{80})} - 750^{f(750)} \right) |
</math><sup>[[Bibliography:_Specific_energy_consumption_models|Morrell, 2004]]</sup> |
</math><sup>[[Bibliography:_Specific_energy_consumption_models|Morrell, 2004]]</sup> |
||
| − | <math>E_{SAG} = 4 \times Mia \left( P_{80}^{ |
+ | <math>E_{SAG} = 4 \times Mia \left( P_{80}^{f(P_{80})} - F_{80}^{f(F_{80})} \right) \times CFsag |
</math><sup>[[Bibliography:_Specific_energy_consumption_models|Morrell, 2004]]</sup> |
</math><sup>[[Bibliography:_Specific_energy_consumption_models|Morrell, 2004]]</sup> |
||
Revision as of 22:45, 25 April 2015
Contents
Morrell SMC SAG & ball mill Model
This is a SAG or AG mill plus ball mill model that estimates the specific energy consumption (ESAG) using the equations of Morrell (2004).
Testwork Required
- The SMC™ test, stored in the "DWT" testwork table (Drop Weight Test).
- Bond ball mill work index. The method requires all the elements of the ball mill work index test to be filled in:
- Ball mill Wi test closing screen size, umclosing, µm
- Ball mill Wi test product size, P80, µm
- Ball mill Wi test feed size, F80, µm
- Ball mill Wi grams per revolution at test conclusion, gpr
Formulae
The method is superficially similar to Bond (among other models), but with a variable exponent on size defined by:
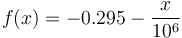
Where x is the particle 80% passing size in µm.
CFsag calibration factor
The CFsag factor is used to reflect the effect of pebble crushing and pre-crushing on the overall circuit performance. This value is automatically selected if you leave this field blank in the model configuration settings.
- Base value, SAB circuit (no pebble crushing, ~6 inch SAG feed), CFsag = 1.00
- Pebble crushing, SABC circuit, CFsag = 0.95
Transfer size
Morrell specifically discourages use of transfer size in calculations such as those in SAGMILLING.COM for a variety of reasons (see discussion in Morrell, 2011). Unfortunately, the alternative method proposed by Morrell is a complex equation that requires pre-selected mill sizes and a series of unpublished calibration factors. This alternative method is not practical for the calculations in SAGMILLING.COM, so a transfer size approach is used instead.
The modelled transfer sizes are probably "Bond-compatible" and not similar to what would be measured directly in a plant survey. Plant survey results would need to be subjected to a phantom cyclone calculation before they are comparable to the model predictions.